How Long Is Residency by Specialty?

27963 Views
Residency is a stage of medical training that, in the US, is completed after medical school. As post-graduate medical education, residency training ranges in length depending on what field you are training for. Additionally within each field, there are opportunities to specialize even further through an added few years of fellowship training following residency.
Deciding Factors When Choosing a Specialty
Deciding on which specialty to pursue will depend on multiple factors. Some may be drawn to the operating room while others prefer working in an outpatient clinic setting. In contrast, some may want to focus on specific patient populations or organ systems. A survey conducted by the Association of American Medical Colleges in 2019 found that 42% of residents considered length of training as an important deciding factor when choosing their specialty. Although the length of training should not be the primary factor in choosing a specialty path, it may still contribute to your decision.
Factors that Contribute to the Length of Residency Programs
Certain specialties involve a separate first year, also known as PGY-1 or intern year, which consists of a “clinical base year” involving rotations through a range of specialties to provide a broad base of training. The next few years of training are then dedicated to that specific specialty. Residency programs can have openings that are categorical positions, meaning that the program provides the full training including both intern year and specialized training years. Conversely, other residency program spots are advanced positions, meaning the program only provides specialized training following completion of the intern year. In these cases, residents obtain first-year training separately, through a transitional or preliminary year position. These positions may be completed at the same institution or a different institution from the advanced training program.
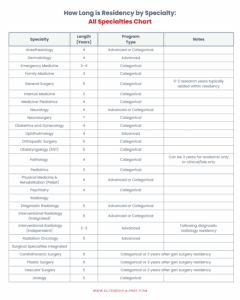
In this blog, we will break down the standard residency training length for each field in the US. In summary, the longest residency, without including any additional research years or further fellowship, is neurosurgery (7 years) and the shortest are for 3 years with family medicine, internal medicine, pediatrics, and emergency medicine (depending on the program).
Anesthesiology
Anesthesiology residency spans a total of 4 years. The first year (PGY-1) consists of a “clinical base year”, explained in depth above. Currently, the majority of anesthesiology residency programs have categorical positions, meaning the full 4 years of training are provided. However, some residency programs offer advanced positions, with the intern year done with a separate program.
Dermatology
Dermatology residency is 4 years in total. Similar to anesthesiology residency, the first year (PGY-1) consists of general clinical training. Most dermatology residency programs currently provide advanced positions only, so completion of a separate transitional year or preliminary year program is required.
Emergency Medicine
The length of training for emergency medicine ranges from 3 to 4 years depending on the program. However, the difference between 3 versus 4 years of training is a topic of debate. Ultimately, the specific program fit and your career or training goals will impact your program selection.
Family Medicine
Family medicine residency consists of 3 years of training. Along with dedicated family medicine clinic and inpatient training, residents also rotate through other primary care services such as general surgery and ob-gyn.
General Surgery
General surgery residency is 5 years. There is also an option to do full-time research years in the middle of the residency, which is becoming more common as more residents pursue surgical fellowships after residency. Certain programs have dedicated research years as a requirement, which can increase the training length to an additional 1 to 2 years.
Internal Medicine
Internal medicine residency training spans 3 years. There is also the opportunity to complete a “chief year” which, unlike other specialties, is an additional year of residency.
Med-Peds
Med-Peds residency consists of a combined residency training for internal medicine and pediatrics over 4 years. Additionally, residents are eligible to take both boards at the end of their training.
Neurology
Neurology residency is 4 years in total. The first year is a general clinical intern year. This may take place in conjunction with the program for advanced training, or at a separate transitional or preliminary year, depending on the neurology program position being categorical or advanced status, respectively.
Neurosurgery
One of the longest residencies amongst medical specialties in the US, neurosurgery residency is 7 years total. Training includes a surgical intern year. Similar to other surgical specialties, residents may have research incorporated into their training, or pursue additional separate research years.
Obstetrics/Gynecology (Ob/Gyn)
The residency for Ob/Gyn is 4 years. Residents receive training in both obstetrics and gynecology.
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology residency is 4 years, which also consists of a general PGY-1 intern year. The majority of ophthalmology programs have categorical positions, which provide both an intern year and 3 years of ophthalmology training – the included intern year allows for earlier integration of ophthalmology rotations in your first year of residency.
Orthopedic Surgery
Orthopedic surgery residency is a total of 5 years. The first year consists of one year of general surgery training, before starting 4 years of dedicated training for the specialty.
Otolaryngology (ENT)
Residency for otolaryngology is 5 years. As part of a categorical program, residents typically complete one year of general surgery training followed by 4 years training related to ear, nose, and throat surgeries.
Pathology
Pathology residency typically consists of 4 years to include both anatomic pathology and clinical/laboratory pathology. Some institutions may also offer specialized training in just one area/division for 3 years (anatomic pathology or clinical/laboratory pathology).
Pediatrics
Pediatrics residency has a 3-year training period. Of note, pediatric hospital medicine is now considered a subspecialty, requiring a 2-year fellowship after residency before becoming board-certified.
Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (PM&R)
PM&R residency involves one intern year and 3 years of specialty training for 4 years total training. Majority of PM&R programs currently are advanced positions only, so a separate intern year is completed typically in medicine, surgery, family medicine, or transitional years.
Psychiatry
Residency training for psychiatry is 4 years in categorical programs, which include a combination of inpatient and outpatient services.
Radiology
Diagnostic Radiology
Diagnostic radiology residency is 5 years total. The first year is a general intern year, but typically involves a significant amount of surgical exposure. Most residency programs are categorical, the few programs with advanced positions only will involve finding a separate transitional or preliminary intern year.
Interventional Radiology
Interventional radiology residency also involves a PGY-1 year of general training, followed by 5 years of specialty training, adding up to 6 years of postgraduate training. An alternative is completing the diagnostic radiology residency followed by 2-3 years of independent interventional radiology training.
Radiation Oncology
Radiation oncology residency also spans a total of 5 years. Similar to diagnostic radiology, the first year is a general clinical training year that can consist of a transitional or preliminary intern year, before starting the 4 years of radiation oncology training.
Surgery Specialties Integrated
Some surgical specialties offer integrated residency programs, which may allow residents to start focused training earlier. As of now, these specialties can also be accessed after first completing a surgical residency.
Cardiothoracic Surgery (integrated)
Cardiothoracic surgery integrated residency is typically 6 years of training. If choosing to complete a surgical residency first (typically general surgery, otolaryngology, orthopedics), the independent training is then 3 years.
Plastic Surgery (integrated)
Similarly to cardiothoracic surgery, plastic surgery integrated residency is typically 6 years. If choosing to complete a surgical residency first (typically general surgery, otolaryngology, orthopedics), the independent training is then 3 years.
Vascular Surgery (integrated)
Unlike cardiothoracic and plastic, vascular surgery integrated residency is typically 5 years. If choosing to complete a general surgery residency first, the independent training is then 2 years, making it the shortest residency of all integrated surgery specialties.
Urology
Urology residency is 5 years. Programs are categorical, with the first year being equivocal to a general surgery internship, followed by 4 years of urology training.
Featured Articles
